The implications of this decision will vary by state, depending on how the state regulates ephemeral waters. (Ephemeral waters are waters that present in wet times but vanish in dry times. A permanent wetland can be isolated in dry times, but connected to a lake, river or stream in wet times.) The author of this blog post checked State Departments of Agriculture in the five states now part of the LWV UMRR family. Wisconsin, Illinois, Missouri and Minnesota had no mention of the Sackett decision as of May 29. Iowa Secretary of Agriculture Mike Naig, applauded the decision as bringing needed certainty to farmers. In states where state regulations do not prohibit removing isolated wetlands or preserving ephemeral watercourses, it's reasonable to think that there will be significant pressure to develop or farm in these areas. Even if something like this is allowed now, those who do the developing and farming will still face the reality that water 'seeks its own level', meaning that in large rainfall events or wet seasons these areas will again be inundated and the water will need to be dealt with. Where will this water go?
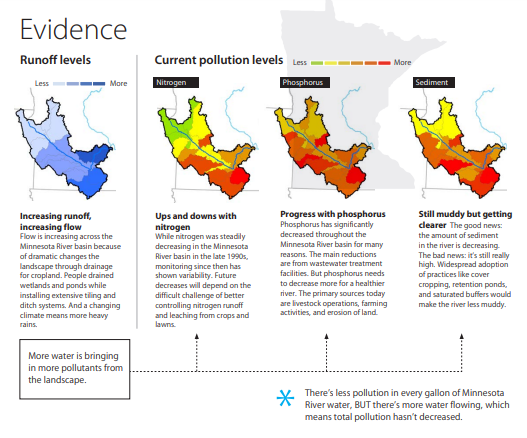
The Minnesota is degraded by excess nutrients and sediments that erode streambanks and bury aquatic habitat. The increased flow in the river due to the drainage of the extensive wetlands that covered the land before European settlement has caused significant damage to the river. Th is has led to the Minnesota being not only a major source of nutrient pollution to the Mississippi, but also being "a river where aquatic life struggles." Rivers and streams across the Midwest are similarly degraded. The Sackett decision can lead to more drainage and more development. This expansion will alter the hydrology, leading to two major concerning outcomes. One will be reducing the time that water has to sink into the soil and replenish groundwater; the other will be the direct discharge of more runoff to surface waters, making them hotter and dirtier. (Want to learn more about the role of groundwater in the hydrologic cycle? Read here.) Hotter and dirtier water will mean more struggles for aquatic life, and less 'fishable and swimmable' waters overall.
Now that the federal government has opened this door, it will be up to individuals, local governments and state leaders across the country to decide how protected our waters will be for the foreseeable future.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
| LWV Upper Mississippi River Region | UMRR blog |


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed